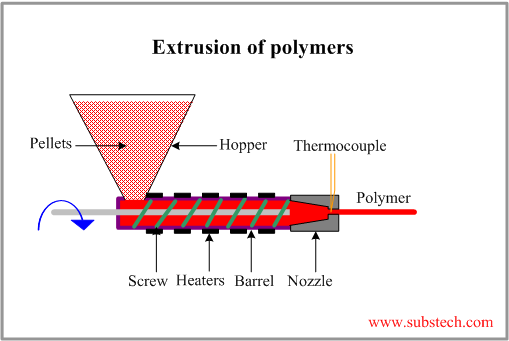
Extrusion is the process by which long straight metal parts
can be produced. The cross-sections that can be produced vary from
solid round, rectangular, to L shapes, T shapes. Tubes and many other
different types. Extrusion is done by squeezing metal in a closed cavity
through a tool, known as a die using either a mechanical or hydraulic
press.
Extrusion produces compressive and shear forces in the stock. No tensile is produced, which makes high deformation possible without tearing the metal. The cavity in which the raw material is contained is lined with a wear resistant material. This can withstand the high radial loads that are created when the material is pushed the die.
Extrusions, often minimize the need for secondary machining, but are not of the same dimensional accuracy or surface finish as machined parts. Surface finish for steel is 3 µm; (125 µ in), and Aluminum and Magnesium is 0.8 µm (30 µ in). However, this process can produce a wide variety of cross-sections that are hard to produce cost-effectively using other methods. Minimum thickness of steel is about 3 mm (0.120 in), whereas Aluminum and Magnesium is about 1mm (0.040 in). Minimum cross sections are 250 mm2 (0.4 in2) for steel and less than that for Aluminum and Magnesium. Minimum corner and fillet radii are 0.4 mm (0.015 in) for Aluminum and Magnesium, and for steel, the minimum corner radius is 0.8mm(0.030 in) and 4 mm (0.120 in) fillet radius.
Extrusion produces compressive and shear forces in the stock. No tensile is produced, which makes high deformation possible without tearing the metal. The cavity in which the raw material is contained is lined with a wear resistant material. This can withstand the high radial loads that are created when the material is pushed the die.
Extrusions, often minimize the need for secondary machining, but are not of the same dimensional accuracy or surface finish as machined parts. Surface finish for steel is 3 µm; (125 µ in), and Aluminum and Magnesium is 0.8 µm (30 µ in). However, this process can produce a wide variety of cross-sections that are hard to produce cost-effectively using other methods. Minimum thickness of steel is about 3 mm (0.120 in), whereas Aluminum and Magnesium is about 1mm (0.040 in). Minimum cross sections are 250 mm2 (0.4 in2) for steel and less than that for Aluminum and Magnesium. Minimum corner and fillet radii are 0.4 mm (0.015 in) for Aluminum and Magnesium, and for steel, the minimum corner radius is 0.8mm(0.030 in) and 4 mm (0.120 in) fillet radius.
Other Topics
IC engine,
Air
Standard Cycles, Method
of Ignition, Gear Types,
mechanical
Engineering, Gears, spur gears,Worm gears,English books,Photoshop
tutorials,Manufacturing,Gears pdf,Computer
science,Harry
potter,Best
100 english books,IC
engine,Metal
Casting,SAND
Casting Quiz,Casting
patterns quiz,Patterns,Mechnical
Previous Years Gate Question Papers ,Mechanical-old-question-paper,Investment
Casting,Workshop
Technology Quiz,Milling
Quiz,Metal
Quiz,Mechanical
Process Quiz,Casting
Process Quiz,Green Sand,Impression
Die Forging,Pricision
Forging,Precision
forgings vs conventional forging,Flashless
forging,Forging
defects,Die
Material for forging of Steel,Cearamic
and Carbide Material for Forging,Forging
Quiz