TYPED BY METHOD OF HEAT TRANSFER
All
of the cooling towers described here are evaporative type towers, in
that they derive their primary cooling effect from the evaporation that
takes place when air and water are brought into the direct contact. At
the other end os the spectrum is the Dry tower, where by full
utilization of dry surface coil sections, no direct contact (and no
evaporation) occurs between air and water. Hence sensible heat transfer
cools the water totally.
IN between these extremes are the plume abatement and water conservation towers, wherein progressively greater portions of dry surface coil sections are introduced into the overall heat transfer system to alleviate specific problems or to accomplish specific requirements
IN between these extremes are the plume abatement and water conservation towers, wherein progressively greater portions of dry surface coil sections are introduced into the overall heat transfer system to alleviate specific problems or to accomplish specific requirements
Other Topics
IC engine, Method
of Ignition, mechanical
Engineering, English books,Photoshop
tutorials,Harry
potter,Best
100 english books,IC
engine,Metal
Casting,Mechnical
Previous Years Gate Question Papers ,Mechanical-old-question-paper,Milling
Quiz,Forging
Quiz,Cold
Extrusion,Hot
Extrusion,CLutch,Wet Clutch,Introduction
to Flywheel,Flywheel:
FACTOR,
Governors ,Thermal
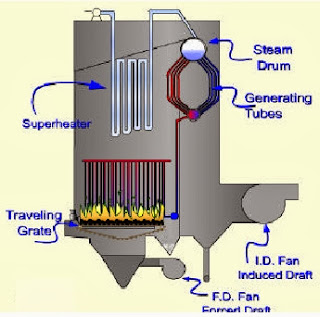
Power Plant,Pulverizer,Boiler,Fire
Tube Boiler,Water
Tube Boiler,Packaged
Boiler,Superheater,Condenser,Types
of Condenser,Air-cooled
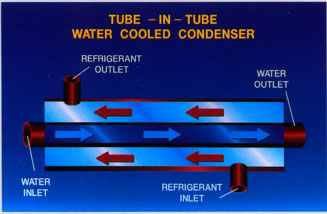
condenser types,Water-Cooled
Condensers,Evaporative
Condensers,TYPES
OF COOLING TOWERS,TYPES
OF COOLING TOWERS,Cooling
Tower: ATMOSPHERIC ,Cooling
Tower:MECHANICAL DRAFT ,Cooling
Tower:HYBRID DRAFT ,Cooling
Tower:CHARACTERIZATION BY AIR FLOW,Cooling
Tower:SPRAY – FILLED ,Cooling
Tower:TYPES BY SHAPE,Cooling
Tower:TYPED BY METHOD OF HEAT TRANSFER