Simple Cycle Power Plants (Open Cycle)
The modern power gas turbine is a high-technology package that is comprised of a compressor, combustor, power turbine, and generator, as shown in the figure "Simple-Cycle Gas Turbine".In a gas turbine, large volumes of air are compressed to high pressure in a multistage compressor for distribution to one or more combustion gases from the combustion chambers power an axial turbine that drives the compressor and the generator before exhausting to atmosphere. In this way, the combustion gases in a gas turbine power the turbine directly, rather than requiring heat transfer to a water/steam cycle to power a steam turbine, as in the steam plant. The latest gas turbine designs use turbine inlet temperatures of 1,500C (2,730F) and compression ratios as high as 30:1 (for aeroderivatives) giving thermal efficiencies of 35 percent or more for a simple-cycle gas turbine.
Other Topics
Hydroelectric
Power Plants,Turbines,Francis
turbine,Kaplan
turbine,Pelton
turbine,IC engine, Method
of Ignition, mechanical
Engineering, English books,Photoshop
tutorials,Harry
potter,Best
100 english books,IC
engine,Metal
Casting,Mechnical
Previous Years Gate Question Papers ,Mechanical-old-question-paper,Milling
Quiz,Forging
Quiz,Cold
Extrusion,Hot
Extrusion,CLutch,Wet Clutch,Introduction
to Flywheel,Flywheel:
FACTOR,
Governors ,Thermal
Power Plant,Pulverizer,Boiler,Fire
Tube Boiler,Water
Tube Boiler,Packaged
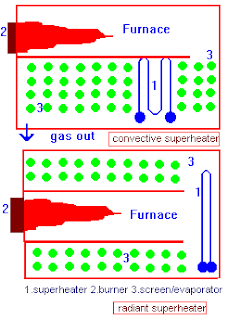
Boiler,Superheater,Condenser,Combined
cycle power plants,Steam
Turbine Power Plants,Combustion
(Gas) Turbines,Simple
Cycle Power Plants (Open Cycle)